技术丨类似Github的webhook实现
-
2020-05-20
Linkflow
所见即所得的企业级客户数据中台(CDP)
本文作者:Linkflow首席架构师 – 王鼎,11年软件研发经验,6年SaaS(基于公有云或私有云),熟悉ERP, CDP, omin渠道销售解决方案。参与SaaS产品的大型开发,成员400余人。在一家初创公司从零开始开发新产品。从事SaaS架构和技术管理工作。建立新的开发团队,专注于CDP和Martech SaaS解决方案。
Webhook是一种非常强大的推送机制,如果熟悉WordPress的同学可以类比构建WP生态的各类钩子函数。Githubt通过webhook让开发人员可以监听仓库的变化触发持续集成工具的运作,比如Travis CI。
需求
大家都看过Github上的webhook,可以对某一个repository设置webhook监听仓库变化,比如push,page_build等event(X-GitHub-Event)。
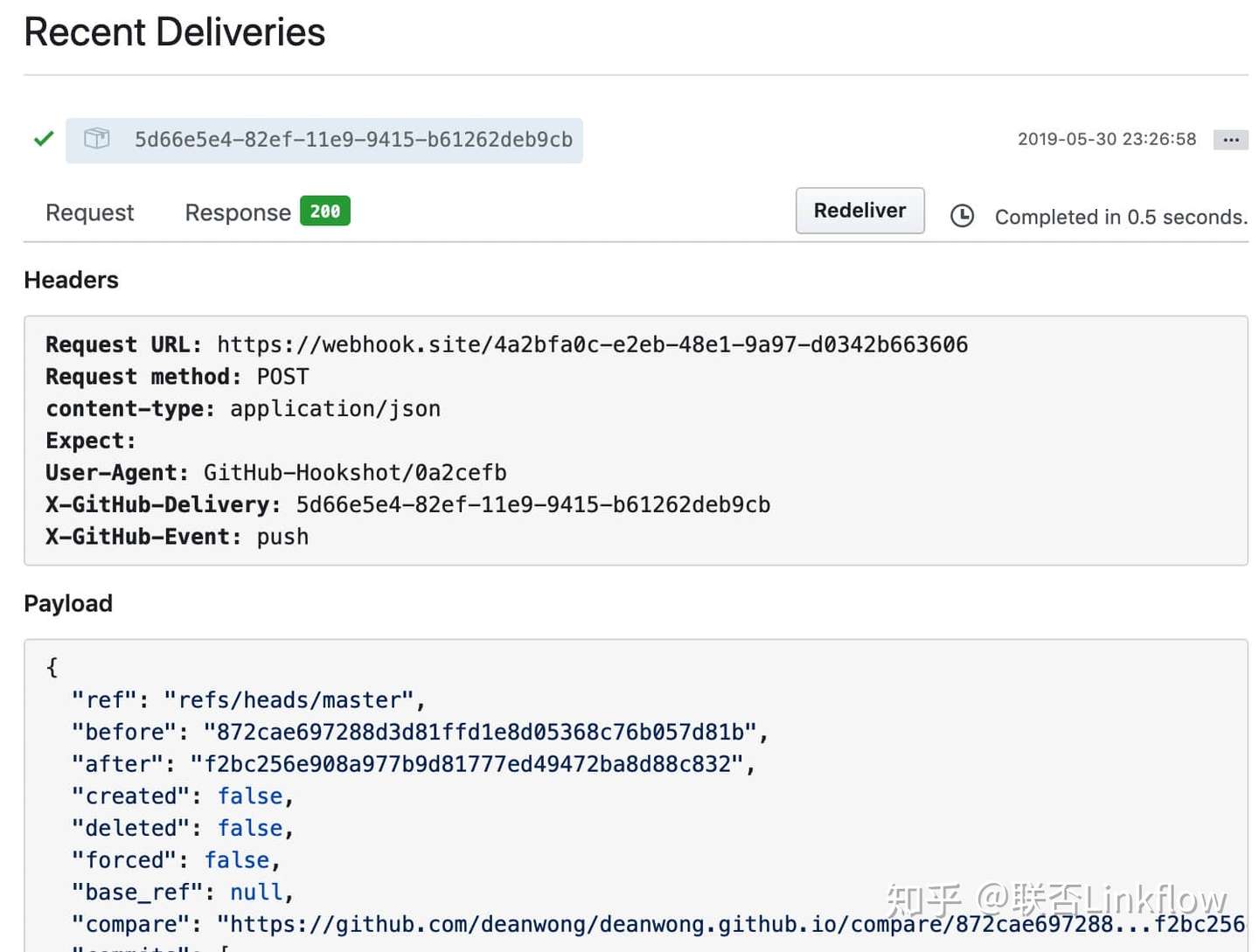
每一次发送都会有个uuid作为标记,并写入到HTTP Header的X-GitHub-Delivery,并且对于发送失败的历史记录,可以点击Redeliver进行重发。
如果把该功能作为一个单独的服务提供方,其根本诉求就是要准确记录到此服务与Internet每一次网络交互的过程,包括发送请求数据和响应结果数据。继续细化,
该服务提供方接收客户端的调用,发送请求到客户端所指定的url并获取响应。
记录每次客户端的原始请求内容(url, method, header, body)以及response(header, body, code, etc.)
需要考虑到客户端重试或重复调用的情况,需要记录每个请求的调用次数以及最后一次调用时间。(客户端调用时可能会传入一个clientId用于接收端去重,如未传服务提供方根据请求生成一个唯一uuid)
提供接口对指定的某个发送历史进行重发。
思考
拿到需求首先要思考一下这个服务会与哪些系统有交互?
请求要发送到指定的URL上,那么第一个交互的系统是某个公网服务。
发送的历史要能保留,说明数据是需要持久化的。第二个交互的系统是数据库。
好了,交互的系统确定后,接下来应该考虑顺序问题,是先发送请求到公网服务还是先操作数据库?我们逐个来分析一下
方案A:先发送请求再将记录写入数据库。问题:如果请求发送了但是数据库写入失败,此时就会造成数据不一致,因为遗漏了发送历史。
方案B:先写入数据库再发送请求。问题:与A类似的,如果数据库写入成功,请求发送失败,比如网络断开等原因。此时数据也会不一致。虽然有了发送历史,但实际发送是失败的。
方案C:先写入数据库接着发送请求最后更新数据。这种方案相对来说比A和B要可靠。第一步写入请求的数据并将状态(status)置为
sending,发送完成再更新status为success或者failure。方案D:先写入数据库,将status设置为
sending,启动一个新的线程扫描该表,对status为ready的记录进行发送,发送完成再更新status为success或者failure。
前两个方案肯定是不可取的,我们来分析一下后两个方案的优劣。方案C的缺点在于第一步写入数据库完成后,发送请求时系统宕机,该记录会一直处于sending状态。好在整体方案会提供一个人工重试(点击Redeliver)的机制,可以事后弥补。优点在于串行化的思维编码比较容易。方案D的优点就是对于一直处于sending状态的历史记录,可以自动进行补发,因为有线程不断扫描。缺点在于这个扫描线程可能会加重数据库的负担。如果要想并行扫描那么又要解决任务分片和编排的问题(参考elestic-job),编码相对较难。
针对以上所述的利弊,最终我们选择方案C。其实把发送网络请求换成发送消息到MQ,那么方案D就很类似大家所熟知的“本地事务表”的解决方案,是将MQ的事务和本地数据库事务绑定的一种思路。
实现
数据结构,定义一个request和response
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
public class WebHookRequest {
@NotBlank
private String url;
private String method;
private Map<String, String> headers;
private String body;
}
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class WebHookResponse {
private String id;
private String data;
private int code;
public boolean isSuccessful() {
return this.code >= 200 && this.code < 300;
}
}
发送方法
public WebHookResponse send(WebHookRequest webHookRequest, String id, boolean retryOnServerError) {
//如果traceId为空则根据请求参数生成一个md5的值作为traceId
if (StringUtils.isBlank(id)) {
//拼接请求参数
String content = webHookRequest.getUrl()
.concat(webHookRequest.getMethod())
.concat(jsonMapper.toJson(webHookRequest.getHeaders()))
.concat(webHookRequest.getBody());
id = DigestUtils.md5Hex(content);
}
// 查找发送记录
WebHookRecord webHookRecord = webHookRecordMapper.findById(id, TenantContext.getCurrentTenant());
if (webHookRecord == null) {
webHookRecord = createFromRequest(webHookRequest);
webHookRecord.setId(id);
try {
// 新建发送记录
webHookRecordMapper.insert(webHookRecord);
} catch (Exception ex) {
LOGGER.warn("Duplicate key for [{}]", webHookRecord.getId());
throw new BizException(B_01000, ex);
}
} else {
// 如果历史已经存在,可能是客户端发送重发请求,那么先判断是否可以重发,sending状态在一定时间间隔内不能重发,避免频繁失败
if (this.shouldResend(webHookRecord.getSendTime(), webHookRecord.getStatus())) {
// 可以重发那么更新状态为sending
this.updateResendStatus(webHookRecord);
} else {
LOGGER.warn("Should not resend key for [{}]", webHookRecord.getId());
throw new BizException(B_01000);
}
}
// 通过网络发送请求,如果失败会直接更新status为failure并抛出异常,发送过程的异常和得到响应对方服务报异常还是不一样的
WebHookResponse webHookResponse = this.doSend(id, webHookRequest);
// 发送完成后更新status
this.onResponse(id, webHookResponse);
if (retryOnServerError && webHookResponse.getCode() >= 500) {
throw new RetryException("server error!");
}
return webHookResponse;
}
/*
* 判断是否可以进行重发
*/
private boolean shouldResend(DateTime sendTime, String status) {
if (!STATUS_SENDING.equals(status)) {
return true;
}
// 发送状态超过60s可重发
return sendTime.plusSeconds(60).isBefore(DateTime.now());
}
/*
* 调用网络接口进行发送
*/
private WebHookResponse doSend(String id, WebHookRequest webHookRequest) {
//调用httpClient
String responseBodyString = null;
Response response;
try {
response = webHookIntegrationService.send(webHookRequest.getUrl(),
webHookRequest.getMethod(),
webHookRequest.getHeaders(),
webHookRequest.getBody());
if (response.body() != null) {
responseBodyString = response.body().string();
}
} catch (Exception ex) {
this.onSendFailed(id, ExceptionUtils.getStackTrace(ex));
throw new RetryException("http send error!", ex);
}
return new WebHookResponse(id, responseBodyString, response.code());
}
/*
* 请求正常返回后的处理
* 这里有一个乐观锁的问题,如果同时有多个线程调用改办法修改同一个历史请求,只有一个线程会更新成功
*/
private void onResponse(String id, WebHookResponse webHookResponse) {
WebHookRecord webHookRecord = webHookRecordMapper.findById(id, TenantContext.getCurrentTenant());
webHookRecord.setResponse(webHookResponse.getData());
webHookRecord.setResponseCode(webHookResponse.getCode());
//更新状态
if (webHookResponse.isSuccessful()) {
webHookRecord.setStatus(STATUS_SUCCESS);
} else {
webHookRecord.setStatus(STATUS_ERROR);
}
int count = webHookRecordMapper.updateResponse(webHookRecord);
if (count == 0) {
LOGGER.warn("Attempt to update WebHook id={} with wrong version ({})", id, webHookRecord.getVersion());
}
}
/*
* 再次发送时更新状态 (真正发送网络请求前)
*/
private void updateResendStatus(WebHookRecord webHookRecord) {
webHookRecord.setStatus(STATUS_SENDING);
webHookRecord.setSendTime(DateTime.now());
int count = webHookRecordMapper.resend(webHookRecord);
if (count == 0) {
throw new OptimisticLockingFailureException("Attempt to update WebHook id=" + webHookRecord.getId() + " with wrong version (" + webHookRecord.getVersion() + ")");
}
}
为了避免对于同一个请求有多个线程同时发起重试的问题,我们在updateResendStatus方法上使用了乐观锁,如果其中一个线程更新状态成功,那么其他线程会因乐观锁问题直接失败,不会走到真正发送网络的请求的那步。也就是说在发送网络请求前过滤绝大部分并发问题。
最后,可以使用一个单元测试,模拟并发请求进行验证。
@Test
public void testMultiThreads() throws InterruptedException {
//调用send接口
WebHookRequest webHookRequest = new WebHookRequest();
webHookRequest.setUrl("http://www.qq.com");
webHookRequest.setMethod("POST");
Map<String, String> headers = new HashMap<>(1);
webHookRequest.setHeaders(headers);
int nLoop = 100;
String clientId = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(nLoop);
Runnable task = () -> {
try {
givenToken().when().body(webHookRequest).post("/webhooks/send?clientId=" + clientId)
.then()
.statusCode(HttpStatus.OK.value())
.extract()
.response();
} finally {
countDownLatch.countDown();
}
};
ExecutorService executorService = new ThreadPoolBuilder.FixedThreadPoolBuilder().setThreadNamePrefix("thread-webhook").setPoolSize(100).build();
for (int i = 0; i < nLoop; i++) {
executorService.execute(task);
}
countDownLatch.await();
int times = webHookMapper.findById(clientId, 1L).getTimes();
// 验证数据库里记录的发送次数是否 等于 真正调用发送网络请求接口的次数
Mockito.verify(webHookIntegrationService, Mockito.times(times)).send(Mockito.any(),
Mockito.any(), Mockito.any(), Mockito.any());
}
总结
如果想进一步提升性能,可以使用支持异步的httpclient工具包,onResponse在callback中进行处理。
整体来说,这是个很简单的小需求,但要考虑周全其实还是要费一番功夫的。究其本质就是异构系统间的数据一致性问题。当我们把发送网络请求换成写数据到redis,到MQ,到另一个微服务时,就会发现它们存在的共通性。一次请求涉及多个系统,并且无法包裹进同一个事务,就会产生这样的问题。至于解决方案是二阶段提交,事后补偿,还是自动对账,就要根据自己的业务特点来选择了。
-
本文作者:Linkflow
责任编辑:马亚蒙
本文来源:牛透社
-
分享到:




















